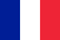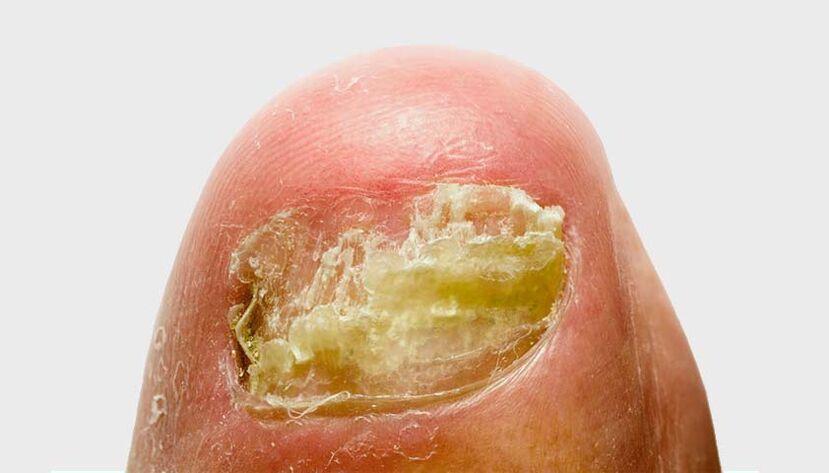
- Nail injuries;
- Wearing tight, non-breathable shoes for long periods of time;
- Live in hot, humid climates.
- Patient age: This disease is more common in people over 40 years old;
- overweight;
- decrease in immunity;
- Related diseases: diabetes, thyroid disease, varicose veins;
- Flat feet and other foot deformities;
- Long-term use of certain drugs: antibiotics, cytostatics, corticosteroids.
Family factors play a special role in the spread of onychomycosis. According to statistics, 55% of patients have a family history of onychomycosis.

Causes of onychomycosis
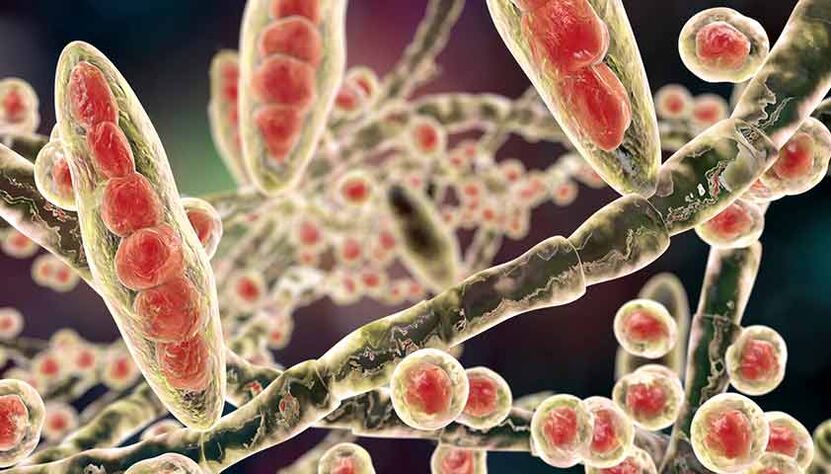
Types of onychomycosis
- Normal nutrition: there is no change in the shape of the nail plate, but white and yellow stripes are visible in the thickness of the nail;
- Hypertrophy: The deck is significantly thickened, brittle, and has jagged edges;
- Dystrophy: The nail plate thins and detaches from the nail bed.
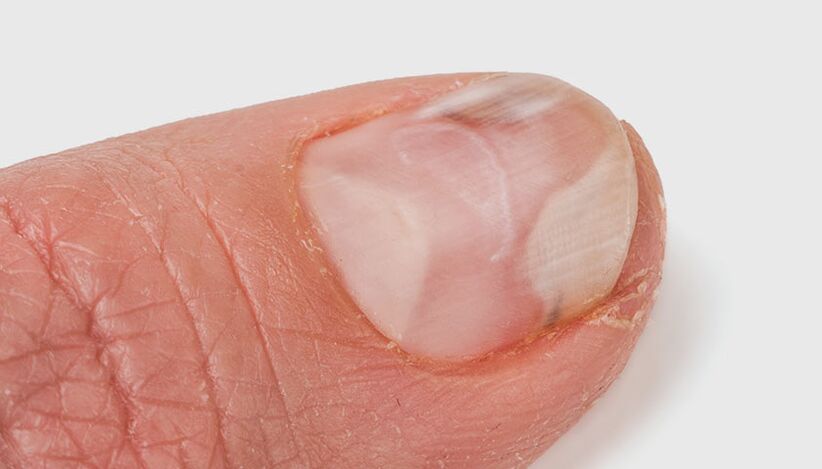
- Light white: Fungus colonizes the upper part of the nail plate. White lesions appear on the nails. As the infection spreads, the nails turn gray-brown and begin to crumble;
- Distal-lateral subungual: The fungus invades the skin in the area of the nail fold or free edge of the nail. The nail plate thickens, yellows, crumbles, and then detaches from the nail bed;
- Proximal subungual: The fungus spreads from the skin and nail folds into the nail plate and deeper. Spots appear in the holes in the nails and in the nail bed area. Loss of nail plate;
- Complete malnutrition: The entire deck is affected. It looks sharply thickened and takes on a dirty yellow color. The nail surface becomes uneven.
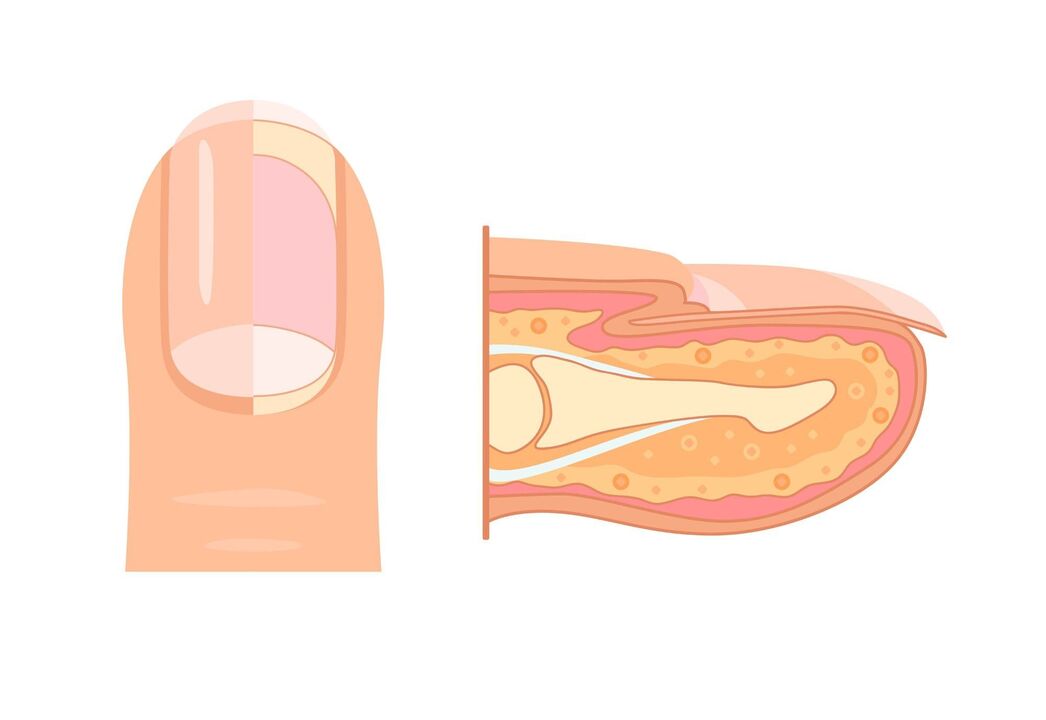
Symptoms of onychomycosis
- Nail plate color changes to yellow, black, green, brown, or gray;
- Separation of the nail plate from the nail bed;
- changes in nail plate thickness;
- Onychomycosis - Nails become concave, teaspoon-shaped;
- Onychomycosis - Nails curved like a raptor's beak;
- Thickening of the nail bed;
- Changes in the surface of the nail plate: formation of pits, grooves, ridges;
- Nailfold inflammation.
Complications of onychomycosis
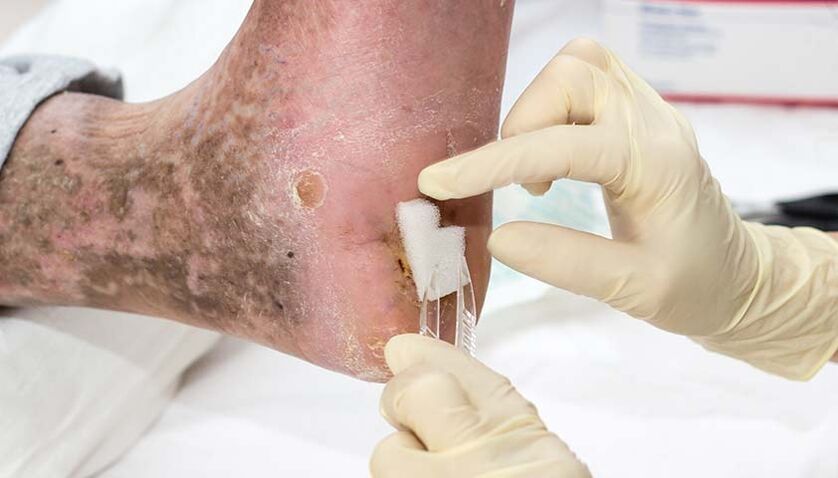
- diabetic foot;
- allergic reactions;
- Chronic erysipelas of the extremities is an infectious skin lesion;
- Lymphostasis - Retention of lymph fluid in tissues;
- Elephantiasis (elephantiasis) is a progressive lymphedema in which subcutaneous fat tissue is replaced by connective tissue.
Diagnosis of onychomycosis
Treatment of onychomycosis
- antifungal agents;
- Antiseptics – antifungal and antibacterial;
- Multiingredient medications may also contain anti-inflammatory substances.
Prediction and Prevention
- Change socks every day, or more often if your feet are sweaty or damp;
- Allow shoes to dry after wearing;
- Please do not wear shared slippers when visiting;
- Don’t try on shoes in a store barefoot;
- Use a personal towel to wipe your feet;
- Use separate nail care tools (tweezers, files);
- Wear shoes in the pool or sauna;
- Monitor dietary diversity;
- Avoid stressful situations.