Symptoms of foot fungus
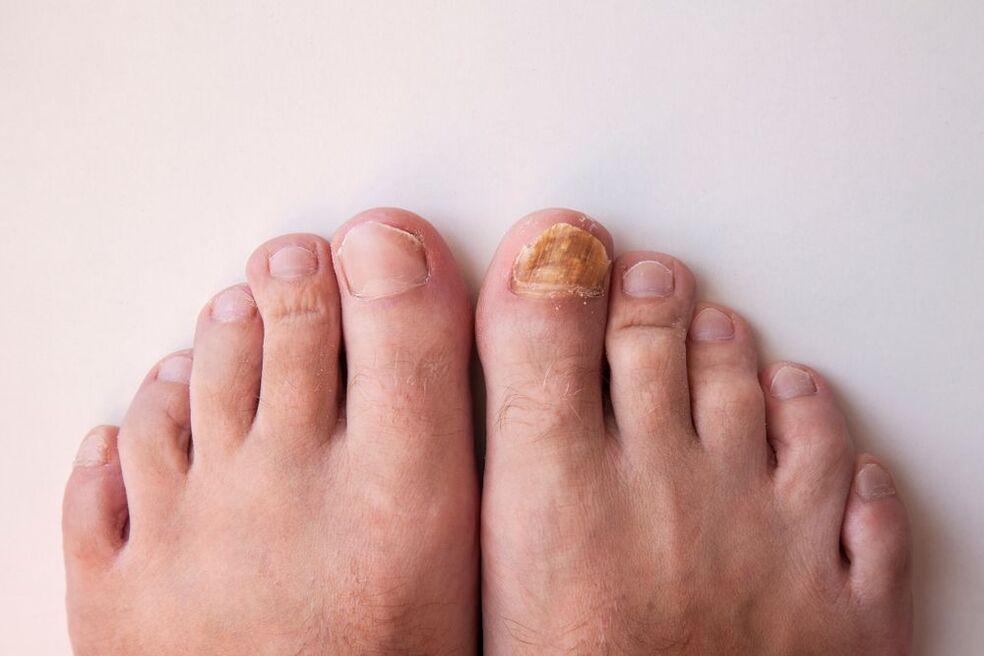
Dermatophytosis of the feet
Yeast-like mycoses of the feet
foot mycosis
Causes of foot fungus
- Increased sweating of the feet.
- Chronic illness exists.Diabetes, certain blood disorders, and long-term use of antibiotics or immunosuppressive drugs can cause fungal infections and spread the disease to other parts of the body.
- There were microtraumas to the legs.Small cracks and cuts are a direct route to infection. Therefore, it is very important to immediately treat the damaged skin area with an antiseptic.
- Failure to observe hygiene rules.Walking without shoes in public places (bathrooms, saunas, swimming pools) can easily lead to fungal infection.
Ointment for treating foot fungus
- Broad spectrum antifungal effect
- Triple action on fungal cells
- Reduces itching, inflammation and antibacterial effects
- Good penetration into affected skin areas and long-lasting antifungal effect due to lipophilicity
- May be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the unborn baby
Prevent foot fungus
- Disinfecting Shoes During Treatment for Foot Fungus
- Maintain personal hygiene and do not walk barefoot in public places (swimming pools, saunas, baths)
- Don't wear other people's shoes
- Choose shoes according to the season, preferably ones made of natural materials.
- Treat new wounds and cuts promptly
- Use products to reduce foot sweating