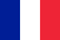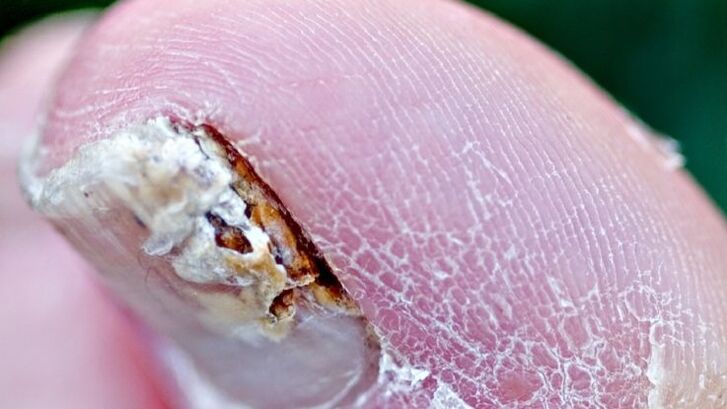
Factors leading to onychomycosis
- Increased sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Insufficient blood supply to blood vessels. Violation of the structure and tone of veins, especially those of the lower limbs (typical of toenail onychomycosis).
- age. The incidence of human disease increases with age. In 15-20% of the population, the pathology occurs between 40 and 60 years of age.
- Internal organ diseases. Disrupts the nervous, endocrine (onychomycosis most common in patients with diabetes) or immune (immunosuppressed, especially HIV infection) systems.
- Large nail patches, consisting of a thick nail plate and its underlying contents, can cause discomfort when wearing shoes.
- trauma. Persistent trauma or injury to the nails without proper treatment.
disease prevalence
The increased prevalence of the disease may be related to increased use of tight-fitting shoes, increased use of immunosuppressive treatments, and increased use of public locker rooms.
Onychomycosis pathogens
onset

adhesion
Several recent studies have investigated the molecular mechanisms by which arthrospores adhere to keratinized surfaces. Dermatophytes have been shown to selectively use their proteolytic reserves during adhesion and invasion. After adhesion occurs for some time, the spores germinate and enter the next stage - invasion.
Invasion
Owner's reaction
Although epidemiological observations suggest a genetic predisposition to fungal infections, there are no molecularly confirmed studies.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms of toenail and fingernail injuries
Distal-lateral subungual onychomycosis
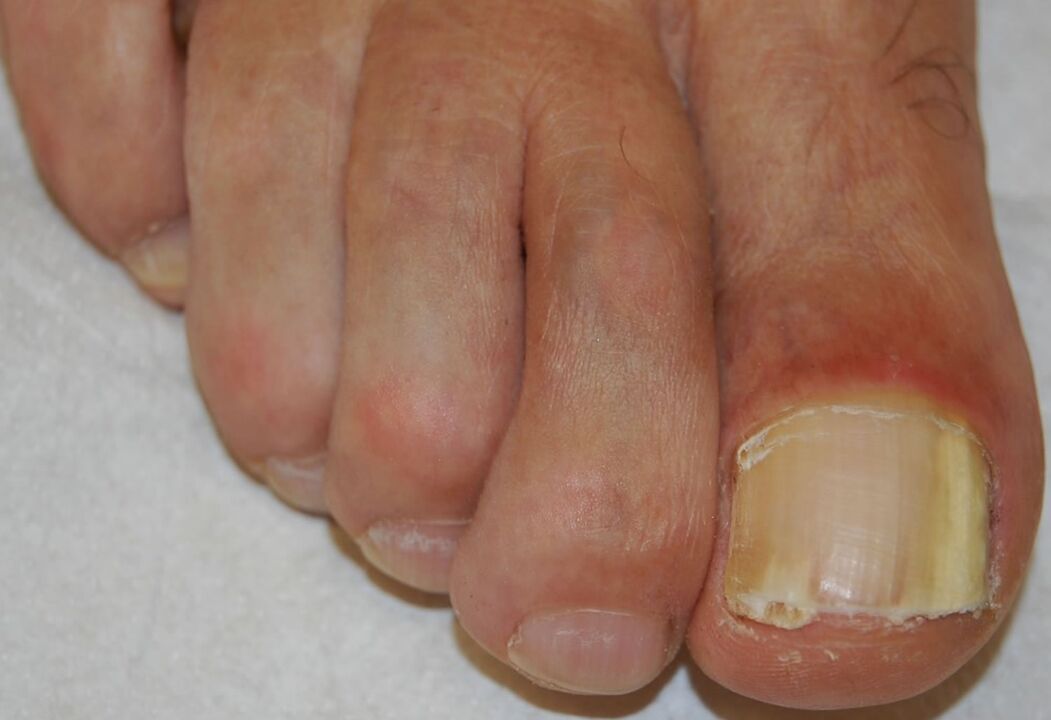
proximal subungual onychomycosis
Patients with proximal subungual onychomycosis should be investigated for HIV infection, as this form is considered a hallmark of the disease.
White superficial onychomycosis
Candida onychomycosis
Diagnosis of onychomycosis
Learn with CON
The most reliable way to reduce false negative results due to sampling error is to increase sample size and repeat sampling.
cultural analysis
- If dermatophytes were isolated in culture, they were considered pathogens;
- Non-dermatophyte mold or yeast organisms are isolated in culture only if hyphae, spores or yeast cells are observed microscopically and recurrent active growth of the non-dermatophyte pathogen is observed without isolation. related.
Histopathological examination
Differential diagnosis of onychomycosis
| most likely | sometimes possible | rarely found |
|---|---|---|
|
|
melanoma |
Onychomycosis treatment
Topical antifungals
Varnishes from the oxypyridone group are gaining in popularity, applied once daily for 49 weeks, with about 40% of patients achieving mycological cure and 5% of cases of mild or moderate onychomycosis caused by dermatophytes achieving nail cleansing (clinical cure). Although much less effective than systemic antifungals, topical use of this drug avoids the risk of drug interactions. Another drug was specially developed in the form of nail polish to be used twice a week. It is a representative of the new antifungal drug morpholine derivatives, which is effective against yeast, dermatophytes and molds that cause onychomycosis. This product may have a higher mycological cure rate than previous varnishes; however, controlled studies are needed to determine a statistically significant difference.
Oral antifungal medications
Allylamine drugs have inhibitory and fungicidal effects on dermatophytes and Aspergillus, but are less effective on Scopus genus. This product is not recommended for candidal onychomycosis as its effectiveness against Candida species varies. For most toenail injections, a standard dose of 6 weeks is effective, while toenail injections require at least 12 weeks. Most side effects are related to digestive problems and include diarrhea, nausea, taste changes, and elevated liver enzymes. Data show that a 3-month continuous dosing regimen is currently the most effective systemic therapy for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis. Clinical cure rates in various studies are around 50%, but rates are higher in patients over 65 years of age. An azole drug with fungistatic activity against dermatophytes and non-dermatophyte mold and yeast organisms. Safe and effective treatment options include daily pulse dosing one week per month or continuous daily dosing, both of which require two months or two cycles of treatment for nails and at least three months for toenail lesionsor three pulse treatments. For children, drug doses are given individually based on body weight. Although the drug has a broader spectrum of action than its predecessor, studies have shown that it has significantly lower cure rates and higher relapse rates. Liver enzyme levels increased during treatment in less than 0. 5% of patients and returned to normal within 12 weeks of stopping treatment. A drug with fungicidal activity against dermatophytes, certain non-dermatophyte molds, and Candida spp. This medication is usually taken once a week for 3 to 12 months. There are no clear standards for laboratory monitoring of patients receiving the above drugs. It makes sense to perform a complete blood count and liver function tests before treatment and 6 weeks after starting treatment. Due to the long course of treatment, potential side effects, drug-drug interactions, and relatively low cure rates, drugs in the grisan group are no longer considered standard treatments for onychomycosis.
Other medicines
Surgery
Many doctors believe that the primary and primary method of treating onychomycosis is mechanical nail removal. In most cases, surgical removal of the affected nail is recommended, and in a few cases, removal with a keratolysis patch is recommended.
Traditional ways to fight onychomycosis
Course and prognosis
prevention
- Disinfection of personal and public items.
- Systematically disinfect shoes.
- Treat feet, hands, folds (under favorable conditions - the most preferred location) with local antifungal medicines according to the advice of a dermatologist.
- If onychomycosis is diagnosed, you will need to see your doctor for monitoring every 6 weeks and after completing systemic treatment.
- If possible, your nail plate should be disinfected every time you visit your doctor.